Virtual Reality in Manufacturing: What are the Key Considerations?
Essential Insights for using VR Simulations to Build Real-Time, Immersive Workflows for Manufacturing Processes

Virtual reality (VR) is transforming the manufacturing landscape, offering powerful tools for design, prototyping, and process optimization. As more companies embrace this technology, the benefits of VR—such as faster development cycles, enhanced collaboration, and reduced costs—are becoming clear. However, implementing a successful VR strategy in manufacturing requires careful planning. From selecting the right hardware and software to aligning teams and processes, this blog explores the key considerations to ensure your VR investment delivers maximum value.
What are the Advantages of Using VR technology in Manufacturing?
The use of virtual reality (VR) offers numerous benefits to manufacturers, revolutionizing how companies design, prototype, and streamline their processes. One of the key benefits is the ability to visualize and interact with 3D models in real-time, allowing engineers to identify design flaws early, reducing the need for costly physical prototypes. VR also enhances collaboration across teams by enabling virtual walkthroughs and simulations, regardless of geographical location.
Additionally, VR can improve training by immersing workers in realistic, safe environments where team members can practice assembly, maintenance, or operational tasks before stepping onto the factory floor. Ultimately, VR accelerates decision-making, cuts development costs, and fosters innovation by providing a more intuitive, immersive approach to product and process development.

How can VR be used in Manufacturing?
Virtual reality is revolutionizing the way manufacturers approach every stage of production, from product design to assembly and maintenance. By creating immersive, real-scale environments, VR allows engineers to virtually test and refine processes before a single physical prototype is built. VR can be leveraged to validate critical aspects of manufacturing including:
Product Integration
How do you know your product is properly designed for assembly, maintenance/servicing, and operations?
Virtual reality expedites product development by allowing product engineering teams to validate integration strategies early in the process. By digitally evaluating packaging, clearances, space claim, and mechanism design, engineers can anticipate and address potential issues for assembly, maintenance, and servicing operations.
Realistic physics simulations enable the examination of wiring, cabling, and hoses in real-scale and real-time, identifying and preventing issues such as tangling, binding, or pinching that could lead to interference, collision, or abrasion during operation.
Assembly Processes
How can you evaluate different assembly scenarios early enough to accelerate the start of production?
Plan assembly operations early and safely, without waiting for a physical mock-up. Effective Virtual Reality software offers realistic physics immersed in a virtual world enabling leading OEMs and their suppliers to validate tooling early and with confidence. They anticipate assembly line and cell layout for optimization of their manufacturing facilities to make sure they reach their deadlines for the start of production and ramp-up phases.
First-hand experience in VR lets you evaluate operator visibility, reachability, and accessibility during assembly or build. When combined with Digital human models (DHM or manikins) representing the anthropometry of your choice, will let you analyze ergonomics of your experience, to ensure safe and efficient assembly processes, well ahead of production.
Maintenance Processes
How can product service engineers realistically evaluate their maintenance processes before products are manufactured? when will they find out if an operation is difficult or dangerous to perform as designed?
Using virtual reality technology enables OEMs to evaluate and validate maintenance procedures and required tools, well ahead of product launch, while problems are less costly to correct. The immersive, real-time, real-scale experience gained helps manufacturers integrate human interactions into their process definition as early as possible to achieve maximum process efficiency.
For Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO) companies or OEMs providing on-site repair, Virtual Reality helps prepare maintenance interventions taking account of local constraints, helping them define safe and efficient ad-hoc processes.
But before you get started on working on any of the above…
What do Organizations Need to Think About Before Implementing a VR Strategy?
When rolling out a VR strategy on an enterprise scale, its not as simple as putting on a headset, grabbing the controllers and off you go. Buy-in needs to come from a number of different areas across the business as the implementation will ultimately involve multiple stakeholders.
So here are some useful things to consider:
Have Clear Objectives and Use Cases
- Define your specific goals for VR adoption, such as improving design validation, optimizing product development, or reducing physical prototyping.
- Identify practical use cases where VR will deliver the most value—whether for virtual assembly trials, maintenance simulations, or collaborative design reviews.
Without properly outlining these, you will struggle to create a scalable and sustainable strategy. Once identified within your organization, you’ll then be able to clearly address the rest of the considerations outlined below…
Cost and ROI Evaluation
- Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to understand the initial investment and ongoing costs of VR implementation, including hardware, software, and training.
- Measure the return on investment (ROI) by tracking improvements in design accuracy, product quality, time-to-market reductions, and cost savings (not only monetary, but operational in terms of the people, preparation, part order and iterations that are associated) from reduced physical prototyping.
Pilot Testing and Scalability
- Begin with a pilot project over 3 to 6 months to test the feasibility of VR in your specific use case and environment, gathering feedback from users to identify the real proof of value from running such a project before scaling the initiative.
- Plan for scalability, ensuring the VR solution can be expanded to other departments or regions as adoption grows.
How will VR Integrate with your Existing Systems
- Ensure the VR solution integrates seamlessly with your existing CAD, PLM, and ERP systems to avoid data silos.
- Compatibility with other digital tools and workflows is essential for efficiency, especially when working with large design models or real-time simulations.
User Training and Adoption
- Plan for user training to help employees across different roles—engineers, designers, and operators—adapt to VR technology.
- Identify potential challenges in user adoption, especially for non-tech-savvy employees, and offer tailored support and education programs.
Hardware and Software Requirements
- Invest in the appropriate VR hardware, such as headsets, motion tracking sensors, and haptic feedback devices, based on the your organization’s specific needs (e.g., immersive training or design validation).
- Evaluate the scalability and performance of VR software, ensuring it can handle complex 3D data models and real-time interactions.
Collaboration and Remote Work Capabilities
- Consider how VR can facilitate collaborative work, especially in global or distributed teams, enabling multiple users to interact with virtual models simultaneously.
- Leverage VR for remote problem-solving, design reviews, or troubleshooting without the need for in person meetings.
User Safety and Ergonomics
- Ensure that VR environments are designed with user safety in mind, avoiding disorienting experiences or prolonged exposure that could lead to discomfort.
- Implement best practices for ergonomics to minimize strain on users during prolonged VR sessions, which is crucial for training or operational simulations.
Data Security and IP Protection
- Protect sensitive data and intellectual property within the VR environment, especially when sharing virtual models or collaborating across multiple locations or organizations.
- Ensure the VR platform has robust security features, such as encryption and access controls, to prevent unauthorized access to design files.
By addressing these considerations, an organization can successfully implement a scalable VR strategy that enhances productivity, collaboration, and innovation.
Future Outlook: Virtual Reality and the Manufacturing Industry in 2025
As we look towards 2025, the use of virtual reality technology in the manufacturing industry is poised for significant advancements and will continue to bridge the gap between digital and physical environments. Emerging trends include the integration of artificial intelligence with VR, enabling predictive maintenance and intelligent process optimization.
Haptic feedback systems are expected to revolutionize virtual prototyping, allowing designers and engineers to feel and manipulate digital models with unprecedented realism. This development will further reduce the need for physical prototypes.
Moreover, as sustainability and efficiency become more critical, VR will support the industry's drive towards reducing material waste, minimizing errors, and speeding up time-to-market
The rise of 5G networks will facilitate real-time collaboration in VR environments across global teams, accelerating design iterations and problem-solving. Additionally, VR-powered digital twins will become more sophisticated, offering an efficient way to monitor and control factory operations remotely.
These innovations promise to transform manufacturing processes, boosting productivity and fostering innovation in product development and creating smarter, more adaptable production ecosystems.
Manufacture your Future in Virtual Reality with IC.IDO
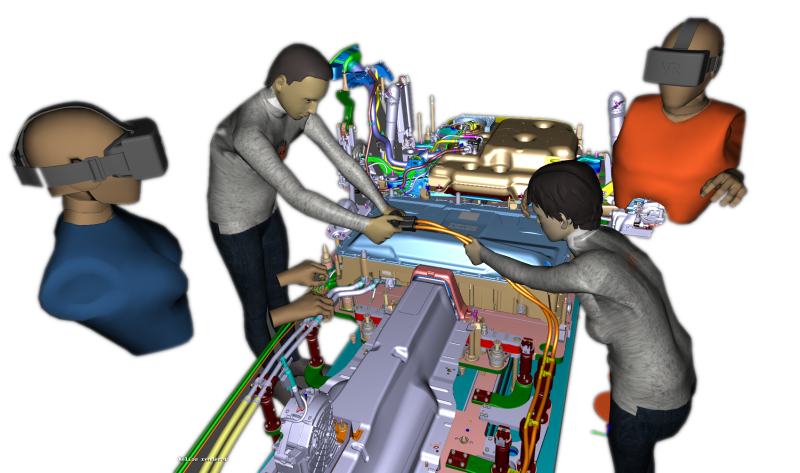
IC.IDO is ESI's Virtual Reality software platform that is revolutionizing product development and process optimization by enabling collaborative virtual workflows.
By immersing teams in high-fidelity, full-scale virtual mock-ups, IC.IDO allows enterprises to experience future products, evaluate integration, and optimize human-centric processes long before physical production environments are available.
This proactive approach helps identify potential issues early in the development process, when design changes can still be made without incurring dramatic costs or delays, ensuring more efficient and effective product designs.
To find out more about what IC.IDO can do for your organization, check out the dedicated IC.IDO webpage.
Katharine Edmonds is a Content Marketing Specialist at ESI Group, and has spent the past 9 years working in marketing and communications for SaaS providers in the engineering and manufacturing industries. Katharine leans on her knowledge and experience of CAD, PLM and eXtended Reality (XR) technologies to create engaging and informative content that champions the benefits of virtual prototyping, and bridges the gap between complex technical subjects and a broader audience.