End-to-End, AI-powered Simulation Drives Airbag Development
How ESI's VPS software for airbag simulation provides a comprehensive approach to airbag development, ensuring accuracy and productivity.

As the automotive industry pursues more connected and autonomous vehicles, manufacturers must navigate stringent safety regulations and the constant need to innovate while cutting costs and speeding time to market. Traditionally, engineers have relied on physical testing; however, that approach is no longer viable - technically or economically. Critically it fails to evaluate the full spectrum of potential crash scenarios and passenger locations. This puts virtual simulation in pole position to optimize vehicle performance, increase productivity and meet stringent safety standards.
The Pivotal Role of Airbags Deployed in Vehicle Safety
Airbags need rigorous, predictive testing to ensure they deploy effectively and protect occupants in both regulatory and consumer crash test scenarios. Due to the numerous crash scenarios and the variety of occupant sizes and genders that must be accounted for in airbag development, physical tests alone cannot cover everything. As a result, safety requirements are increasingly being evaluated using numerical simulation during the design process. Virtual Prototyping software plays a crucial role, as the accuracy of predictions and the ability to quickly obtain simulation results are essential for effectively utilizing airbag simulations in automotive projects.
Benefits of Virtual Simulation for Airbag Development and Test:
- Cost-effective: Minimizes the need for physical prototypes, delivering significant savings.
- Faster development: Early virtual simulation speeds up design cycles, boosting productivity.
- Higher accuracy: Evaluate fluid and structure interaction for a detailed understanding of materials, gas behavior, and impacts.
- Enhances safety: Allows testing of complex simulations, ensuring better occupant protection.
Make the Difference in Accuracy and Speed with Virtual Performance Solution (VPS)
VPS is recognized as the industry’s most precise simulation software. It helps automotive OEMs improve vehicle quality, safety, and reliability while minimizing development time and costs. VPS enhances efficiency, accelerates innovation and improves the accuracy and reliability of designs by offering a comprehensive package with airbag folding, airbag deployment capabilities, advanced fluid-structure interaction technology, and AI-driven productivity tools.
The fully digital workflow capabilities, coupled with folding simulation, provide airbag suppliers and OEMs with an end-to-end development solution. This unique combination enables engineers to thoroughly and accurately model every aspect of the airbag from folding through to deployment. A great example is Toyoda Gosei.
By using ESI Virtual Performance Solution’s airbag module for airbag folding and sewing, the accuracy and lead time for developing complex Knee Airbag (KnAB) have improved drastically.
Alexander Diederich,Group Leader at CAE Toyoda Gosei Europe
Stage 1 | Airbag Folding
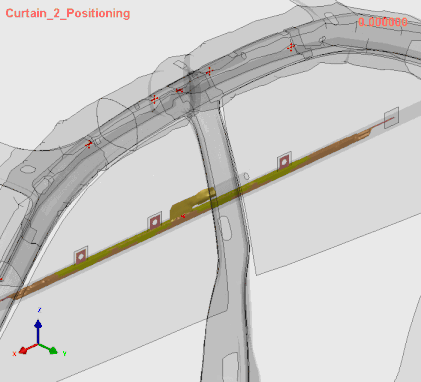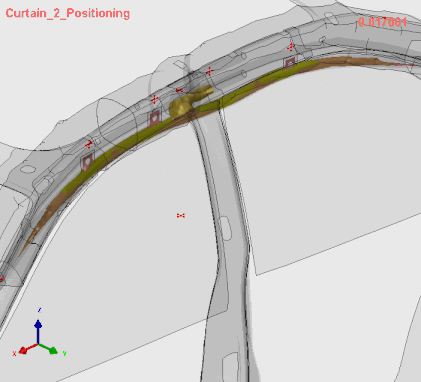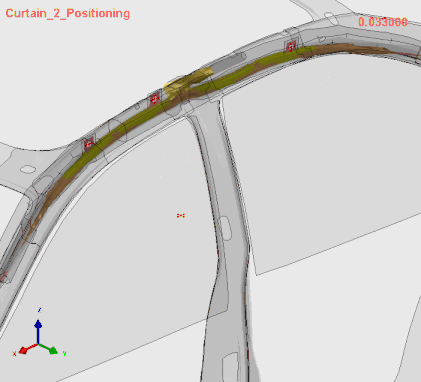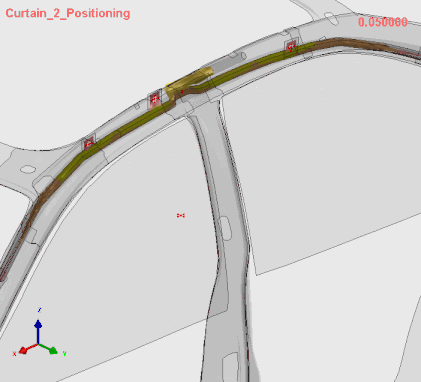
Airbag Folding Simulation in VPS SimFolder, (C) ESI Group, a part of Keysight Technologies, 2025
The SimFolder module accurately simulates even the most complex airbag folding processes by replicating the physical process. This ensures highly precise folded bag geometry, which is essential for predicting airbag deployment effectively.
Stage 2 | Airbag Deployment
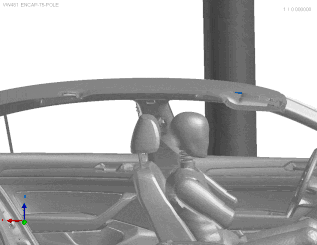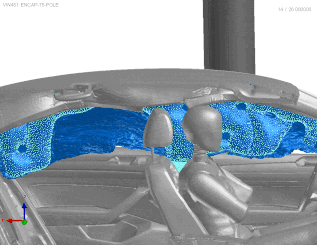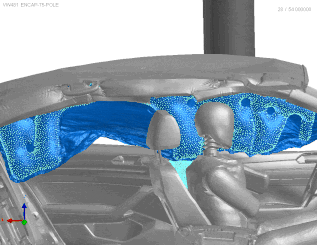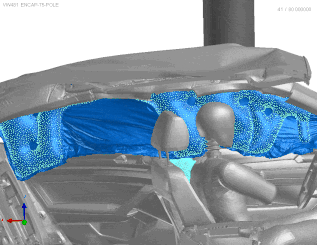
VPS airbag deployment simulation, (C) ESI 2025
VPS utilizes the Finite Pointset Method (FPM) to simulate airbag deployment. This method ensures highly accurate results, especially in the critical first milliseconds. This is essential for out-of-position scenarios as well as side and curtain airbags. FPM is used for gas flow simulation, while Finite Element Analysis (FEA) handles structural analysis. This approach predicts how the airbag will unfold and interact with both occupants and the vehicle, even in complex scenarios.
Additionally, the software optimizes computing resources, speeding up simulations and boosting productivity. During the initial deployment, non-uniform pressure simulation with FPM captures pressure variations across the airbag. Later, the model switches to uniform pressure to simulate the fully inflated airbag to save CPU time.
With four decades of proven track record in the automotive industry, ESI's VPS software delivers precise airbag deployment kinematics through unique, advanced fluid-structure interaction capabilities, ensuring accurate simulations even for out-of-position and side-impact scenarios. From fast folding to deployment simulations, our software has continuously raised the bar for accuracy in airbag development projects.
Stage 3 | Understanding Full Car Crash Model
Additionally, the simulations can be integrated into a full car crash model, where all airbags are deployed simultaneously. This is achieved with reasonable CPU times, balancing high fidelity results with performance. The latest FPM technology enhances the accuracy of side curtain airbag deployment, where precise sequencing is vital to protect the occupant’s head during impact—enhancing safety and driving a more efficient design process.

Full Car Virtual Testing in VPS, (C) ESI 2025
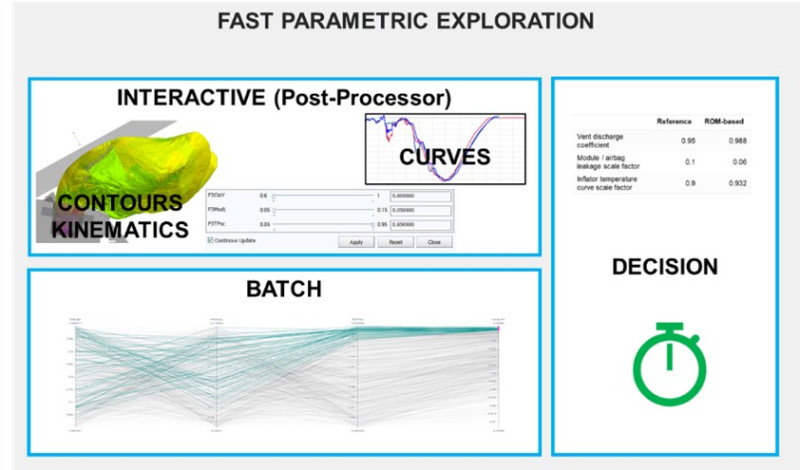
Accelerating Airbag Model Calibration with AI
The calibration of airbag model parameters such as outflow discharge coefficient, inflator heat loss, which may not be measured precisely by tests, is one particular application that requires extensive and time-consuming iterations. This impacts validation quality and delivery time of airbag models for the synthesis car crash simulations. The choice of relevant airbag model parameter exploration range for validation is based on experience and trial & error approach. It is limited by the computational cost of high-fidelity CFD coupled Finite Element simulation runs.
Productivity gains can be significantly enhanced with AI and Reduced-order-modeling (ROM) techniques: ROM-based methodology reduces the airbag validation time by testing thousands of parameter combinations in a time frame of days instead of weeks. Therefore, model quality can be improved as more combinations can be tested using Reduced Order Modelling than within Finite Elements standard approach.
The process for finding the best parameters sets among more than 1000 combinations is fully automated and takes less than one hour. Those batch exploration and automatic calibration capabilities can slash project time, with some ESI customers reporting a decrease from three weeks to three days.
Time to Transform Your Airbag Development
Curious to learn how ROM can help achieve this goal? ESI, alongside Volkswagen and global airbag suppliers have been working on an industrial airbag calibration study. Join us at two upcoming events where we'll explain the available ROM methods, including Proper Generalized Decomposition (PGD), and dive into the choice of Design of Experiments (DOE) and the required number of Finite Element simulations for training the ROM model. Don’t miss out!
Visit ESI at CAE Grand Challenge 2025
See us as NAFEMS World Congress 2025
Alain Trameçon has more than 30 years of experience in the development, research, innovative industrial projects, and software solution management of numerical simulation. He is a technical expert in Fluid-Structure Interaction and Composite Crash for ESI Virtual Performance Solution (VPS) Virtual Prototyping software. Together with his team, he developed and validated industrial solutions for simulating complex phenomena such as airbag deployment and automobile water crossing. Today, he leads the Pre-Certification & Validation outcome solution team for crash, NVH, and acoustics.